线程不安全类与写法
StringBuilder线程不安全示例
@NotThreadSafe
public class StringNoSafe {
// 请求总数
private static int clientTotal = 10000;
// 并发数
private static int threadTotal = 100;
public static StringBuilder stringBuffer = new StringBuilder();
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringNoSafe test = new StringNoSafe();
// 使用并发库,创建缓存的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 创建一个Semaphore信号量,并设置最大并发数为
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
// 希望所有线程结束再返回主线程,所以是请求总数
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
// 创建10个任务,上面的缓存线程池就会创建10个对应的线程去执行
for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) {
final int NO = i; // 记录第几个任务
int finalI = i;
Runnable task =
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire(); // 获取许可
appendStr();
semaphore.release(); // 释放许可
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
};
executor.submit(task); // 执行任务
}
try {
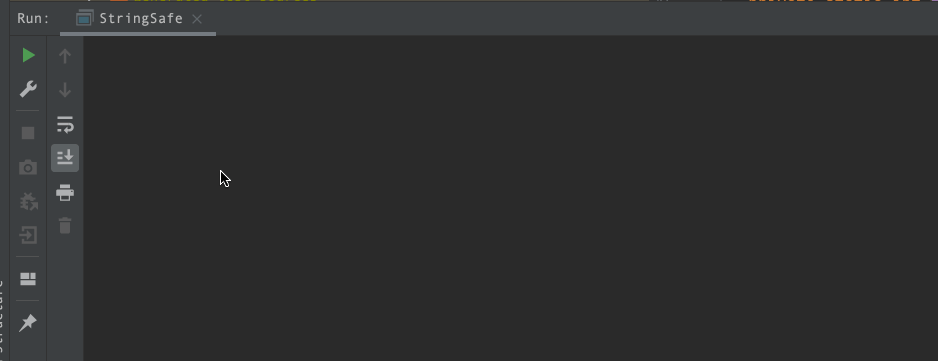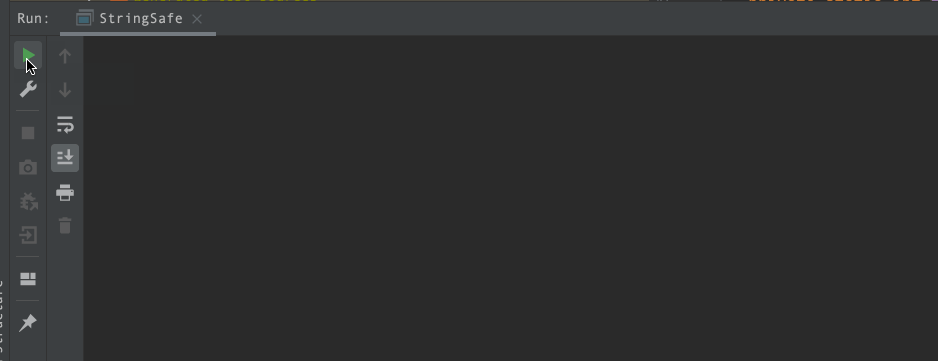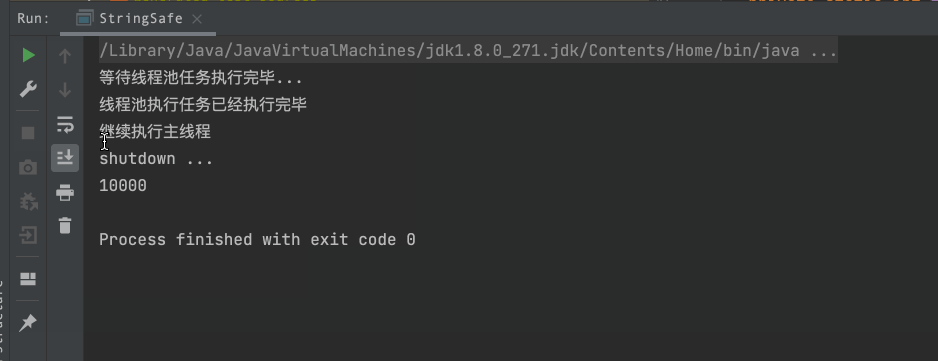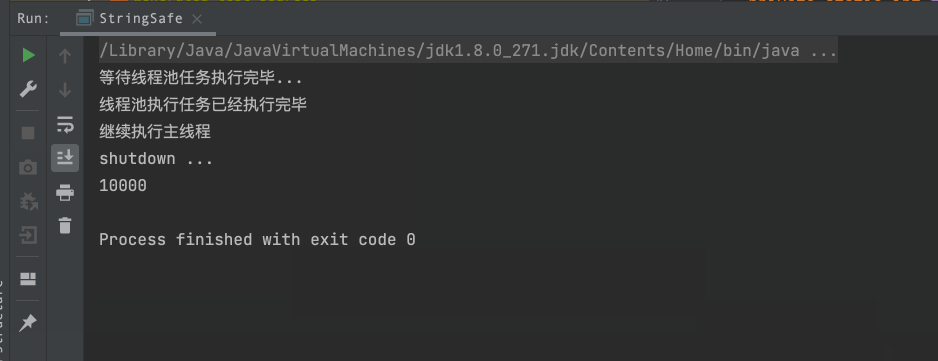
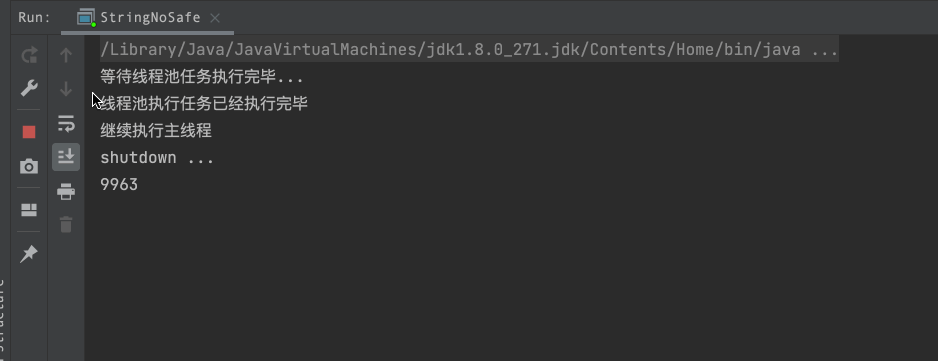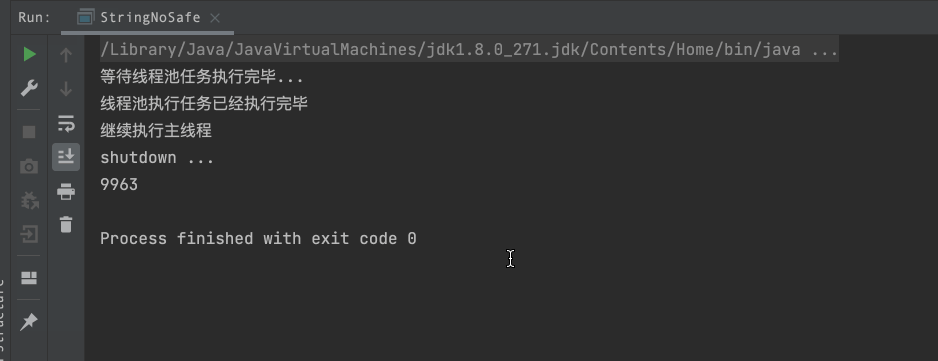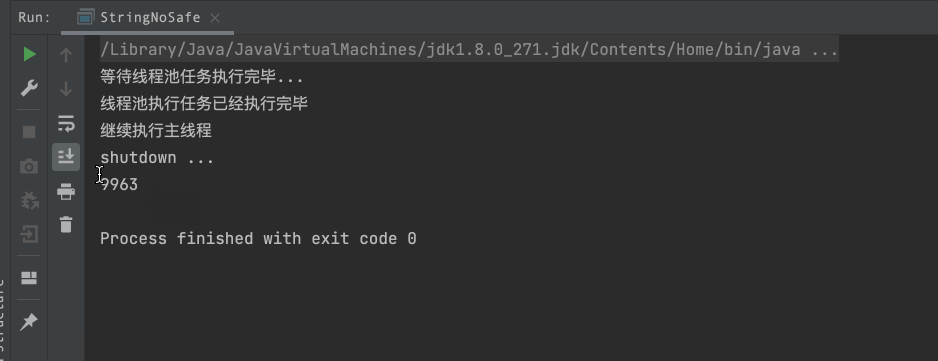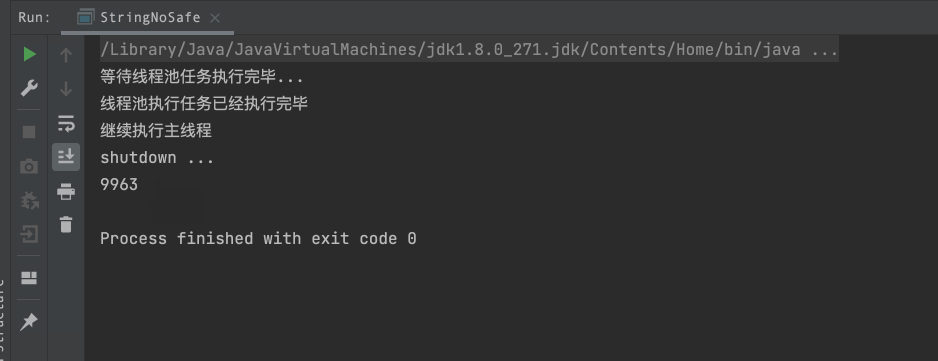
System.out.println("等待线程池任务执行完毕...");
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("线程池执行任务已经执行完毕");
System.out.println("继续执行主线程");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!executor.isShutdown()) {
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("shutdown ...");
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer.length());
}
private static void appendStr() {
stringBuffer.append("a");
}
}
解决办法
package top.xiongmingcai.stringexample;
import top.xiongmingcai.annoations.ThreadSafe;
import java.util.concurrent.CountDownLatch;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.Semaphore;
@ThreadSafe
public class StringSafe {
// 请求总数
private static int clientTotal = 10000;
// 并发数
private static int threadTotal = 100;
public static StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer();
public static void main(String[] args) {
StringSafe test = new StringSafe();
// 使用并发库,创建缓存的线程池
ExecutorService executor = Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
// 创建一个Semaphore信号量,并设置最大并发数为
final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(threadTotal);
// 希望所有线程结束再返回主线程,所以是请求总数
final CountDownLatch countDownLatch = new CountDownLatch(clientTotal);
// 创建10个任务,上面的缓存线程池就会创建10个对应的线程去执行
for (int i = 0; i < clientTotal; i++) {
final int NO = i; // 记录第几个任务
int finalI = i;
Runnable task =
new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
semaphore.acquire(); // 获取许可
appendStr();
semaphore.release(); // 释放许可
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
};
executor.submit(task); // 执行任务
}
try {
System.out.println("等待线程池任务执行完毕...");
countDownLatch.await();
System.out.println("线程池执行任务已经执行完毕");
System.out.println("继续执行主线程");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
if (!executor.isShutdown()) {
executor.shutdown();
System.out.println("shutdown ...");
}
System.out.println(stringBuffer.length());
}
private static void appendStr() {
stringBuffer.append( "a");
}
}